Roller conveyor design is the foundation that determines the stability, service life, and scalability of material handling systems in factories. At this stage, mechanical and kinematic parameters must be carefully calculated and translated into detailed drawings based on customer requirements and operating environments.
In this article, Belota summarizes the core formulas, technical principles, and key evaluation factors in roller conveyor design, helping businesses minimize risks and optimize operational efficiency.
Why Does Roller Conveyor Design Require Precise Engineering Calculations?
Designing a roller conveyor according to technical standards is a decisive factor for safety, performance, and long-term operating costs of the entire production line. Even a small deviation in one parameter can lead to vibration, product jamming, accelerated wear, or synchronized system failure.

Ensuring Load Capacity and Operational Safety
Proper design determines the correct roller diameter, roller spacing, and frame structure, ensuring stable load-bearing capacity in line with the transported goods. This helps prevent frame deformation, bearing failure, or roller shaft bending.
Minimizing Operational Interruptions
A technically sound design allows smooth conveyor operation with reduced unnecessary friction and resistance. Products move evenly without interruptions, improving productivity and reducing downtime caused by technical issues.
Optimizing Operating and Maintenance Costs
A well-designed system from the outset minimizes uneven wear, bearing damage, shaft bending, or frame failure. This significantly reduces maintenance and replacement costs while avoiding unexpected production stoppages.
In addition, proper engineering design ensures the right selection of materials and configurations, avoiding overdesign that causes unnecessary costs or underdesign that leads to premature failure. Investment costs are optimized while maintaining long-term operational efficiency.
Matching Load Characteristics and Product Types
Each product differs in size, weight, and physical properties. Accurate calculations help select the appropriate roller type (steel, plastic, stainless steel), shaft diameter, bearings, and roller pitch to ensure sufficient load capacity without damaging products.
Key Technical Parameters in Roller Conveyor Design
To design a professional roller conveyor, all technical parameters must be calculated in an integrated manner rather than individually. Each parameter directly affects durability and operational performance.
-
Roller diameter: Determines conveying speed and localized load capacity.
-
Tube wall thickness: Enhances stiffness and resistance to deformation under heavy loads.
-
Roller material: Ensures suitability for the operating environment (corrosion resistance for food processing, wear resistance for mining).
-
Roller spacing: Ensures products are always supported by at least three rollers, preventing jamming or vibration.
-
Roller shaft: Bears the main bending load and ensures concentric, stable rotation at high speeds.
-
Inclination angle (gravity conveyors): Allows products to move smoothly by gravity without excessive speed or impact.
-
Static and dynamic loads: Prevent frame deflection or excessive vibration during real operation.
-
Bearing type: Directly affects smoothness, friction, and service life of each roller.

Professional Roller Conveyor Design Guidelines
Once all design parameters are defined, engineers proceed with overall technical calculations to ensure stable and safe operation. Below is a comprehensive and accurate roller conveyor design guideline.
Selecting Suitable Rollers
Rollers directly contact products, so selection must be based on load capacity, product dimensions, and operating environment.
-
Roller diameter must be sufficient to handle loads and minimize shaft deflection.
-
Common materials include galvanized steel, stainless steel, or plastic depending on dry, humid, or food-grade environments.
-
Bearings and shafts must support loads smoothly with minimal friction to extend system lifespan.

Calculating Roller Spacing
Roller spacing directly affects product stability during transport. A common rule is that products must always be supported by at least three rollers at any time.
Formula: P ≤ Lmin / 3
(Where P is roller pitch and Lmin is the minimum product length.)
-
Small, lightweight products require shorter roller spacing.
-
Large, heavy loads allow wider spacing but still require even load distribution to avoid jamming or deflection.
Designing the Roller Conveyor Frame
The frame bears the main structural load of the system. Key considerations include:
-
Adequate stiffness to prevent vibration during continuous operation.
-
Materials such as powder-coated steel or stainless steel for corrosive environments.
-
Adjustable legs and height matching existing production lines for easy installation.
Designing the Drive System
Depending on application, roller conveyors may be gravity-driven or motorized.
-
For driven conveyors, motor power, operating speed, and torque must match the load.
-
Common drive systems include chain & sprocket, belt drive, or motorized rollers, ensuring smooth operation, low wear, and easy maintenance.
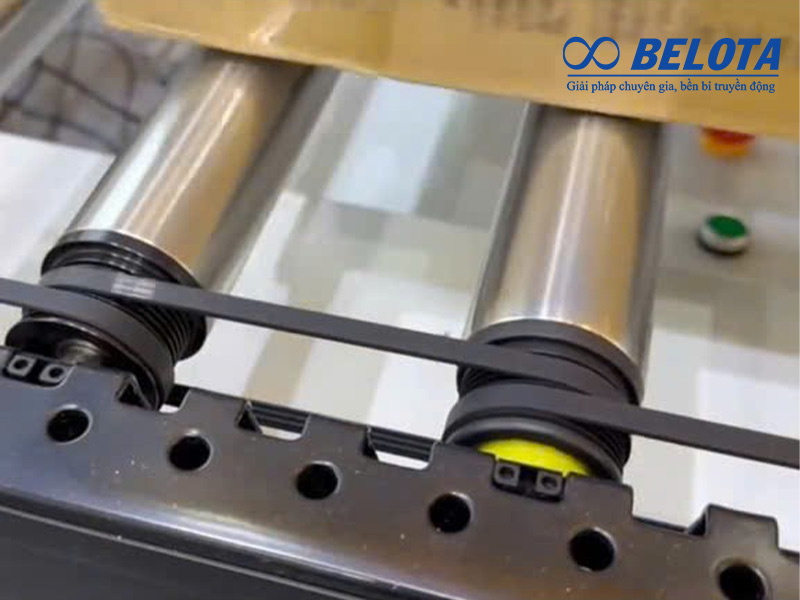

Safety Standards in Roller Conveyor Design
Safety is mandatory in roller conveyor design to protect operators, equipment, and ensure long-term stable operation. Key safety principles include:
-
Guarding moving parts: Drive shafts, chains, belts, and pinch points must be covered to prevent accidents.
-
Structural safety: Frames, supports, and bolted connections must meet high safety factors and withstand maximum loads without deformation.
-
Pinch point control: Proper clearances between rollers and frames to prevent hand or product entrapment.
-
Emergency stop devices: Motorized conveyors must include easily accessible emergency stop buttons.
-
Electrical safety: Motors, control panels, and wiring must meet insulation, grounding, and overload protection standards.
-
Compliance with standards: Apply ISO, ANSI, JIS, or TCVN standards in design and manufacturing.
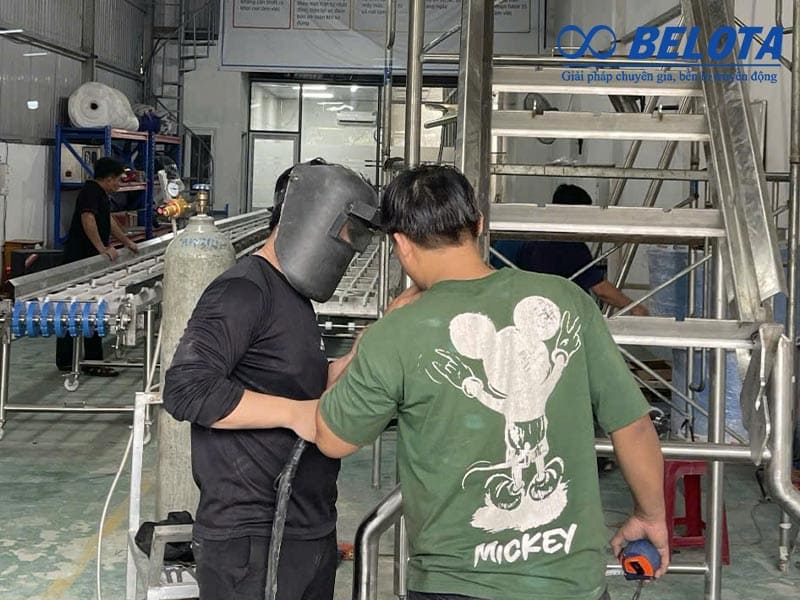

Common Mistakes in Roller Conveyor Design
Many systems require rework after only a few months due to design-stage errors. Common issues include:
-
Excessive roller spacing causing product jamming or tipping.
-
Incorrect motor power calculations leading to overheating or failure under load.
-
Ignoring operating environment, such as using steel rollers in humid conditions, resulting in seized bearings after a short time.
Investing in proper roller conveyor design from the beginning helps businesses avoid repair costs, production interruptions, and unnecessary operational risks.
Roller Conveyor Design Process: From Survey to Handover
A professional roller conveyor design process typically consists of two main stages to ensure accuracy and alignment between drawings and actual installation.
Stage 1: Survey – Consultation – Design
Survey:
Engineers inspect the installation site, measure dimensions, heights, travel direction, and available space. Customers provide detailed information on product dimensions, weight range, base material, environmental conditions, and layout constraints.
Consultation:
Based on survey results, technical teams propose optimal solutions, including conveyor type, frame material, and optional features such as adjustable height, extendable sections, or sensors.
Technical Design:
Engineers prepare detailed 2D/3D drawings showing dimensions, roller positions, motors, gearboxes, supports, and connection points. Drawings are reviewed and approved before fabrication.
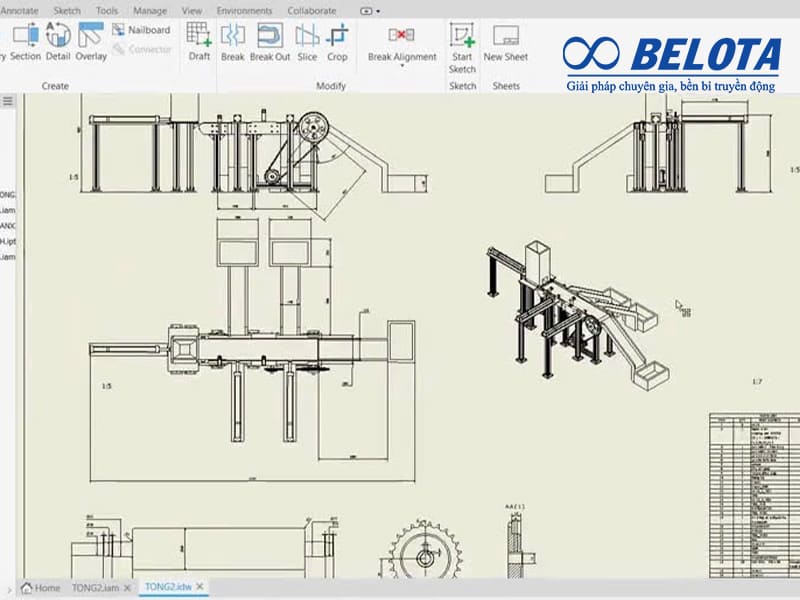
Kỹ sư triển khai bản vẽ 2D/3D thể hiện đầy đủ kích thướ
Stage 2: Fabrication – Installation – Commissioning
Fabrication:
Components are manufactured according to approved drawings. The system is assembled and tested under no-load and full-load conditions to verify stability, noise, alignment, and load capacity.
Installation:
The conveyor is delivered and installed on site, leveled, aligned, and tested under actual operating conditions.
Commissioning:
After successful testing, the system is accepted and handed over to the customer along with operating instructions, maintenance guidelines, and warranty documentation.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the top priority when starting a roller conveyor design?
Product characteristics such as weight, base dimensions, and contact surface.
2. How to choose roller materials for different environments?
Galvanized steel for general logistics, stainless steel for food or corrosive environments, plastic rollers for light loads and quiet operation.
3. What is the ideal roller spacing?
Products should always be supported by at least three rollers to ensure stability.
4. Can roller conveyors integrate with existing automation systems?
Yes. They can easily integrate sensors, VFDs, and PLCs for synchronized operation.
5. Why do design costs vary between suppliers?
Differences stem from material quality, component standards, and long-term reliability considerations.
Conclusion
In summary, a well-engineered roller conveyor design is the foundation for optimized performance and risk control in production systems. Investing in proper consultation and technical calculations from the start ensures sustainable economic efficiency throughout the equipment’s lifecycle. For tailored solutions that match real operating conditions, businesses are encouraged to contact Belota for professional consultation.