Comparison between PU and PVC conveyor belts is a key factor that helps customers select the right belt type, extend conveyor lifespan, and optimize factory operations. In this article, Belota provides a comprehensive overview from basic concepts to in-depth technical analysis offering a complete perspective on the two most widely used conveyor belt materials today.
Materials Used in PU and PVC Conveyor Belts
Any comparison between PU and PVC conveyor belts should begin with a clear understanding of the synthetic polymer materials used in their construction. Identifying the physical and chemical properties of Polyurethane (PU) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is essential to determine their suitability for specific operating environments such as food processing or chemical handling.
PU Conveyor Belts
PU conveyor belts are manufactured from high-grade Polyurethane, known for their excellent mechanical strength, oil resistance, and outstanding durability. They are commonly used in applications where the belt surface directly contacts unpackaged products.

Key Advantages
-
Food safety compliance: PU does not contain harmful plasticizers, is odorless, non-contaminating, and fully complies with strict standards such as FDA and EU Food Grade.
-
High durability and abrasion resistance: Superior resistance to cutting, tearing, and wear compared to PVC, making PU ideal for continuous-operation conveyor systems.
-
Excellent oil and light chemical resistance: Highly effective in food processing environments such as seafood, bakery products, confectionery, meat, and poultry.
-
Wide operating temperature range: Typically from -10°C to 80°C, with some specialized PU belts capable of withstanding higher temperatures for short periods.
-
Various surface finishes: Smooth, matte, rough, diamond-patterned, or textured surfaces to enhance friction and prevent slippage on inclined conveyors.
Limitations
-
Higher initial investment cost compared to PVC conveyor belts.
-
Not suitable for strong chemicals or aggressive solvents, where specialized materials are required.
PVC Conveyor Belts
PVC conveyor belts are made from Polyvinyl Chloride reinforced with fabric layers, offering good flexibility at a more economical price than PU. They are widely used in light industrial applications such as packaging, assembly lines, and logistics, thanks to their versatile thicknesses and surface designs.

Key Features
-
Low initial cost: The biggest advantage, suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises or systems with moderate technical requirements.
-
Good elasticity and flexibility: Ensures stable operation on conveyors with small pulleys and simple mechanical structures.
-
Moisture and water resistance: Performs well in humid environments and cold storage at moderate temperatures.
-
Multiple surface options: Smooth, rough, diamond-patterned, V-cleats, T-cleats—ideal for inclined conveying.
-
Wide range of colors: Green, black, white, gray—easy for line identification and sorting.
Limitations
-
Lower abrasion and oil resistance compared to PU.
-
Narrower operating temperature range, typically from -5°C to 60°C.
-
Not recommended for fresh food contact unless certified food-grade PVC is used.
-
May contain plasticizers, which can compromise hygiene-sensitive environments.
See Also: Detailed Standard Procedure for Rubber Conveyor Belt Splicing
Detailed Comparison Between PU and PVC Conveyor Belts
Analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of PU and PVC conveyor belts helps businesses avoid budget waste and reduce production downtime. Each material performs optimally only when used in the appropriate working conditions.
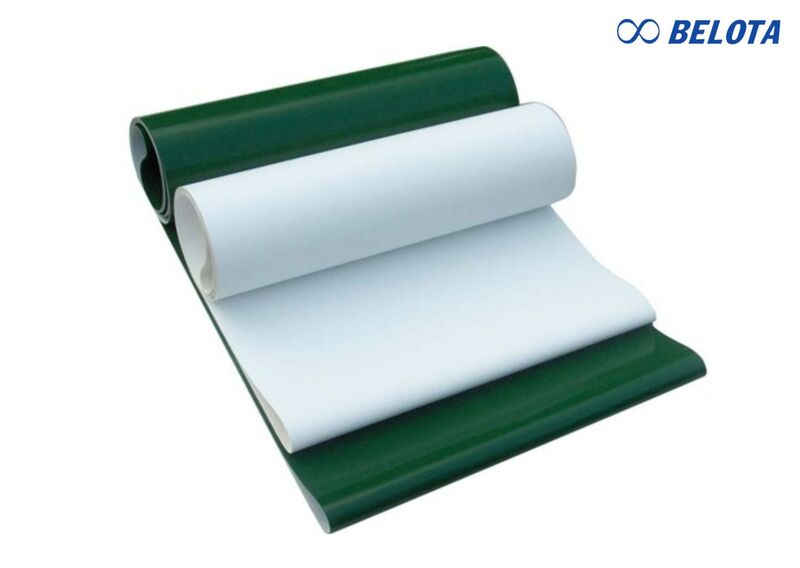

Durability, Load Capacity, and Abrasion Resistance
-
PU Conveyor Belts: High surface hardness, excellent resistance to scratches from metal fragments or sharp objects. Despite being thin, PU belts have exceptional tensile strength and minimal elongation during operation.
-
PVC Conveyor Belts:
Lower hardness, surfaces are more prone to wear over time. Suitable for medium loads, but typically heavier than PU belts.
Chemical Resistance and Temperature Range
-
Chemical Resistance: PU is highly resistant to vegetable and animal oils.
PVC resists only mild chemicals; prolonged exposure to oils can cause swelling, delamination, and belt failure. -
Temperature Performance: PU operates reliably from -40°C to +90°C, making it ideal for deep-freeze environments. PVC performs best between -10°C and +80°C, with reduced flexibility at low temperatures.

Food Safety Standards
This is a critical factor in the food industry.
-
PU: Pure PU materials fully meet food-contact safety standards.
-
PVC: May contain plasticizers and chlorine compounds; improper use in direct food contact can cause chemical migration, affecting food safety and quality.
Cost Considerations
-
PU Conveyor Belts: Higher upfront cost due to premium material and strict manufacturing processes. However, they offer longer service life, lower maintenance costs, and stable long-term performance.
-
PVC Conveyor Belts: Lower initial investment, suitable for limited budgets and light-duty applications. In harsh conditions involving oil, low temperatures, or heavy loads, replacement and maintenance costs may increase.

Quick Technical Comparison Table: PU vs PVC Conveyor Belts
| Criteria | PVC Conveyor Belt | PU Conveyor Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyvinyl Chloride (plasticizers, chlorine) | Pure Polyurethane |
| Abrasion Resistance | Medium (prone to peeling) | Very high |
| Oil Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | -10°C to +80°C | -40°C to +90°C |
| Food Safety | Low risk control | FDA / EU compliant |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High (small pulley compatible) |
| Initial Cost | Low | Higher |
| Cleanability | Moderate | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good with mild acids/alkalis | Moderate |
| Elongation | High | Low |
| Noise Level | Higher | Lower |
| Anti-static Property | Optional | Often integrated |
| Typical Applications | Packaging, logistics, ceramics, wood | Food, pharma, electronics |
When Should You Choose PU or PVC Conveyor Belts?
Selection should be based on operating conditions, hygiene requirements, and long-term investment goals, not just price.
Choose PU Conveyor Belts when:
-
Direct contact with unpackaged products is required
-
High hygiene standards (FDA, EU Food Grade)
-
Presence of oils, moisture, or light chemicals
-
Low or fluctuating temperatures
-
Continuous operation with high durability requirements
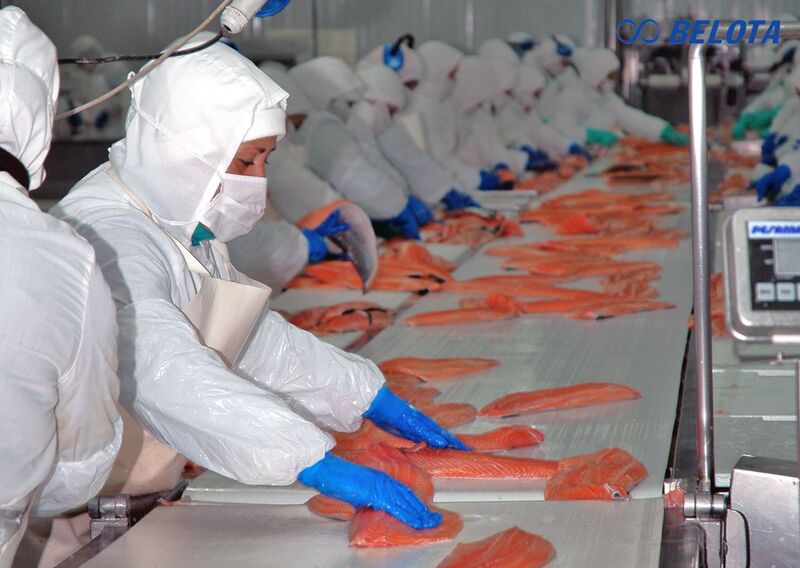
Best suited for: food & beverage, seafood, poultry, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, clean electronics.

Choose PVC Conveyor Belts when:
-
Products are packaged or indirect contact only
-
Dry environments with minimal oil exposure
-
Stable, moderate temperatures
-
Light to medium load systems
-
Budget optimization is a priority
Best suited for: logistics, packaging, printing, assembly lines.

How to Identify PU and PVC Conveyor Belts in Practice
Heat Test
-
PU: White smoke, mild wax-like odor, soft and elastic when heated.
-
PVC: Thick black smoke, strong chlorine odor, carbonized residue.
Surface and Elasticity
-
PU: Smooth or matte surface, flexible even at thin thicknesses (0.8–2 mm).
-
PVC: Thicker (≥2 mm), less flexible, stiffness increases when bent.


Common Mistakes When Comparing PU and PVC Conveyor Belts
-
Focusing only on initial cost
-
Ignoring operating environment specifics
-
Using PVC for direct food contact
These mistakes can lead to higher long-term costs and production interruptions.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why shouldn’t PVC belts be used for unpackaged food?
PVC may release plasticizers and chlorine compounds, posing health and compliance risks.
How to optimize costs when switching from PVC to PU?
Use PU selectively at critical contact points to balance cost and durability.
Does Belota provide material samples?
Yes. Belota offers PU and PVC samples for real-world testing.
Does PU stretch like PVC?
No. PU has excellent dimensional stability and minimal elongation.
Conclusion
This comprehensive comparison between PU and PVC conveyor belts helps businesses make informed decisions. Choosing the right belt material ensures cost efficiency, operational stability, and long-term performance. For tailored solutions, contact Belota for professional consultation.